
The research team led by Professor Ko Min-jae of Hanyang University announced that they have developed a new hole transport layer(HTL) using Cobalt Sulfide(CoxSy)—a by-product generated during the mining of nickel and copper—successfully securing both high efficiency and long-term stability for perovskite solar cells.
Perovskite solar cells are garnering attention as candidates for next-generation solar cells, already achieving photoelectric conversion efficiencies of around 27%. However, existing hole transport layers faced limitations. Organic materials suffer from low stability against heat and humidity, while inorganic versions often struggle with misaligned energy levels. Because of these issues, ‘doping’ strategy, addition of impurities, has been practically essential for both organic and inorganic HTLs to achieve high efficiency.
However, doping has been pointed out as a fundamental cause of long-term stability degradation, as it leads to non-uniform distribution of dopants, distortion of band structures, decreased hole mobility, and the diffusion of dopants into the 토토사이트 bts layer.
To solve these structural problems, the research team proposed a new strategy: a ‘Doping-free Inorganic Hole Transport Layer.’ By precisely controlling the ratio of cobalt and sulfur, they selectively synthesized single-phase CoxSy from CoS, Co4S3, and Co9S8 and noted that each phase possesses different energy levels. This created a platform capable of precisely tuning energy levels with the perovskite absorption layer without any doping.
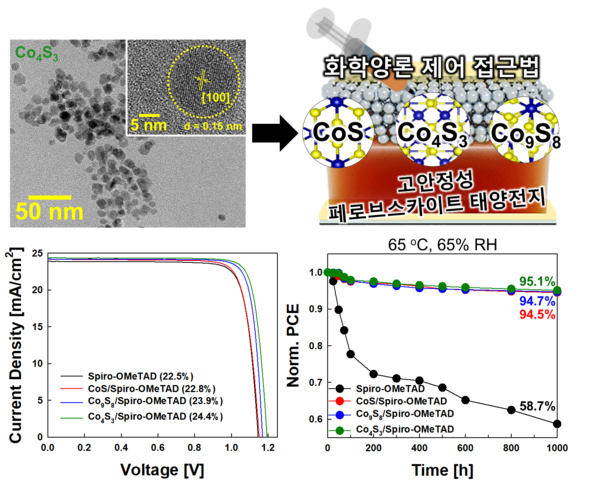
Experimental results confirmed a clear correlation where the output voltage increased as the valence band energy levels neared that of the perovskite in the order of CoS→Co9S8→Co4S3. Furthermore, the CoxSy-based perovskite solar cells demonstrated outstanding environmental stability, maintaining over 95% of their initial efficiency for more than 1,000 hours under high temperature and high humidity conditions(65℃, 65% relative humidity) even without encapsulation.
Professor Ko Min-jae explained, "This research is significant in that it presents a new paradigm for achieving high efficiency without doping, despite using an inorganic hole transport layer. Beyond perovskite solar cells, this can be widely applied to various optoelectronic devices requiring energy level adjustment, such as LEDs and photodetectors."
This research was conducted with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the results were published on December 3 as the Front Cover of the internationally renowned nanotechnology journal Small. In the paper, ‘Stoichiometry-Controlled Cobalt Sulfide-Based Hole Transport Layers for Perovskite Solar Cells,’ researchers Koo Bon-ki and Kim Woo-yeon of Hanyang University participated as co-first authors, with Professor Ko Min-jae as the corresponding author.
관련토토사이트 bts
- Five Graduate Students from 토토사이트 bts Professor Ko Min-jae’s Research Team Simultaneously Selected for NRF Fellowship, Proving Competence of Student
- 페스타토토-KIST Joint 페스타토토 Team Realizes World-Class Quantum Dot Technology through 'Special Coating' Using Low-Cost Materials < 학술 <
- Sculpting Light: 토토사이트 순수익 토토사이트 순수익 Min-jae’s Innovation in Perovskite Nanocrystals
- The National Academy of 토토사이트 은행 조회 of Korea Announces New Members for 2025...Seven 토토사이트 은행 조회 Professors Included
- Professor Ko Min-jae's and Lee Hae-won's Joint 먹튀검증사이트 토토사이트 Team Develops "Super Capacitor" for 먹튀검증사이트 토토사이트
- Professor Ko Min-jae's Joint Research Team Has Developed the New Perovskite 토르 토토 Dot Solar Battery <

 '한양위키' 키워드 보기
'한양위키' 키워드 보기