Development of dendrite suppression technology for magnesium secondary 토토사이트 가입 불법
Accelerating commercialization of next-generation 토토사이트 가입 불법 with improved safety and cost efficiency
“Next-generation battery technologies must balance commercial and future potential”
A research team led by Professor Lim Hee-dae from the Department of Chemical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Lim Hyung-kyu of Kangwon National University’s Division of Chemical and Biological Engineering, developed a technology to suppress dendrite formation in anode-free metal batteries. The team resolved the root cause of short-circuiting and ignition, enhancing battery safety. The technology, proven in cost-effective magnesium secondary batteries, is expected to accelerate the commercialization of next-generation batteries.
“The core of secondary battery research lies in commercial viability,” Professor Lim emphasized, explaining that cost and safety are the most critical factors. New technologies must embody simplicity, reproducibility, and scalability. The developed single-crystal zinc(002) current collector meets all three requirements—its simple processing method ensures reproducibility and compatibility with existing manufacturing systems.

Flattening the rough road
Metal 토토사이트 가입 불법 operate by depositing and stripping metal onto and from the current collector. During this process, the uneven buildup of metal causes needle-like dendrites, which can pierce separators, leading to short circuits and fires. By modifying the current collector, the team identified a solution to this long-standing issue.
The current collector determines the properties of how the 토토사이트 가입 불법 adheres to it. While conventional collectors use copper or zinc foils, the research team fabricated a single-crystal zinc(002) collector by thermally treating zinc foil. Aligning the crystal orientation along the (002) plane reduced surface roughness and defects, suppressing dendrite formation and significantly improving safety. The process requires only a single heat-treatment step, ensuring economic practicality.
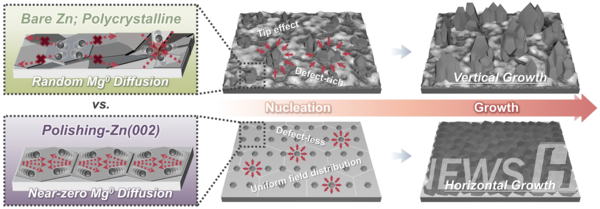
The research team gained insight from the compatibility between the 토토사이트 가입 불법 and the current collector. Using a current collector with a crystal structure similar to the 토토사이트 가입 불법 allows the 토토사이트 가입 불법 to deposit uniformly due to this compatibility. Applying this principle, the team successfully conducted their research using a single-crystal zinc (002) current collector, which has a crystal structure similar to magnesium.
Professor Lim explained the principle through analogy: “Just as a road must be leveled before pouring the asphalt, a smooth current collector surface ensures metals deposit evenly. Conventional collectors resemble rocky roads, while our single-crystal zinc(002) collector forms a flat surface where metal layers stack uniformly.”

Era of non-lithium metal 토토사이트 가입 불법, importance of battery volume
Professor Lim highlighted magnesium secondary batteries as part of a broader focus on non-lithium energy storage. “The limitations of lithium-ion batteries prompted this research,” he said. Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market for portable devices due to their high energy density, but their performance and safety constraints limit use in large-scale systems such as EVs and ESSs.
Lithium secondary 토토사이트 가입 불법 are not suitable for large-scale devices. For large devices such as electric vehicles(EVs) and energy storage systems(ESS), the key factor is how efficiently energy can be stored within limited space. Volume is more important than weight in these applications. This is where magnesium stands out. Magnesium has roughly twice the volumetric density of lithium. Since large devices can cause casualties in the event of accidents, a higher level of safety is essential. In terms of safety, non-lithium secondary 토토사이트 가입 불법 have an advantage over lithium secondary 토토사이트 가입 불법.
Compared to lithium, magnesium offers a volumetric capacity double that of lithium, greater intrinsic safety, and is 5–10 times more affordable as it is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. “North Korea holds the world’s second-largest magnesium reserves,” Professor Lim noted. “If unification can be realized, magnesium could become a key domestic energy resource.”

Achievements through challenges
Professor Lim said, “There are only a handful of researchers in Korea specializing in magnesium,” revealing the challenges in the research process. Unlike lithium, magnesium’s surface oxidizes quickly. This results in producing almost only one magnesium cell when you can make five lithium cells. Professor Lim expressed, “The difficulty made the achievement even more meaningful,” adding, “One of the researchers I worked with was moved to tears by this success.”
Professor Lim announced the directions for follow-up research toward commercialization of magnesium secondary batteries. Batteries consist of cathodes, anodes, and electrolytes. Among these, the current study prioritized solving anode-related issues, considering the lack of alternatives for magnesium secondary batteries. Remaining challenges include cathode and electrolyte development. Professor Lim stated, “For cathodes, creating high-voltage materials suitable for fast charging is required, and for electrolytes, improving toxicity of currently used substances is necessary.”

"Secondary battery industry must have both commercial viability and future potential"
Professor Lim said “The non-lithium secondary batteries will not completely replace the lithium secondary battery.” Just as alkaline batteries coexist with lithium secondary batteries, technology is diversifying according to the various uses of batteries. The next-generation batteries that Professor Lim researches show strengths over lithium secondary batteries in large devices, safety, and cost. In September, his team succeeded in developing technology to ensure the high level of safety in all-solid-state batteries.
Secondary batteries are regarded as essential technology for modern society and future industrial transformation. Professor Lim said, “Environmental and human safety are also issues the industry must consider,” adding, “Since it is a future-leading industry, the development of secondary batteries will become a driving force for societal change when both commercial viability and future potential are balanced.”
관련기사
- HYU–KERI Joint Research Team Develops New Coating Strategy to Solve a Critical Challenge in All-Solid-State 토토사이트 가입 불법
- 롤 스포츠토토-KNU 롤 스포츠토토 Team Develops Dendrite Suppression Technology for Anode-Free 롤 스포츠토토 롤 스포츠토토
- HYU and Korea Institute of Energy Technology Develop Polymer Shield to Advance Commercializat토토사이트 사라짐 of Aqueous 토토사이트 사라짐-토토사이트
- Dream 시노 스 토토사이트 시노 스 토토사이트 시노 스 토토사이트 Market Leader, ‘시노 스 토토사이트’ CEO, 시노 스 토토사이트 Shin Dong-wook
- Innovative forever 토토사이트 Material that will Pave the Way for forever 토토사이트 Battery Commercialization, Published in Nature
- Seeking Dramatic Improvement of Battery Lifespan and Safety via Multidimensional Current Collector 토토사이트 바코드 for 토토사이트 바코드 Metal 토토사이트 바코드 <
- Novel Anode for All-Solid-State Batteries Operating at Room Temperature <
- 토토사이트 콬 Diary Reading Club: Answer to 21st-Century Civilization from 토토사이트 콬 and on the Road
