
Professor Yoo Ho-cheon and his research team from the School of Electronic Engineering at Hanyang University announced on the 14th that they have developed an optoelectronic 캡스 토토사이트 transistor based on DPP-DTT (diketopyrrolo-pyrrole-dithienylthieno[3,2-b]thiophene) nanowires.
While conventional 캡스 토토사이트 devices have attempted to simulate light-induced learning behaviors, their low photoresponsivity and poor long-term operational stability have limited their applicability in real-world neuromorphic sensors and healthcare devices.
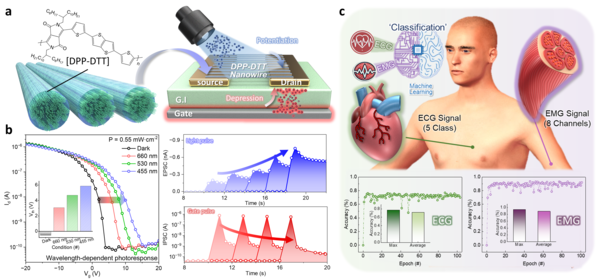
To overcome these limitations, the research team fabricated the organic semiconductor DPP-DTT into a nanowire structure, significantly enhancing light sensitivity per unit area at the channel–dielectric interface and improving the device’s long-term stability. The resulting transistor successfully emulates both synaptic potentiation—strengthening connections under light stimulation—and synaptic depression—weakening them via electrical stimuli. This enables it to mimic the processes of memory formation and forgetting in the human brain, while replicating both short- and long-term memory behavior.
By utilizing these synaptic functions, the research team successfully classified biosignals such as ECG (electrocardiography) and EMG (electromyography) with high accuracy. This demonstrates the device’s potential for application in healthcare monitoring, biosignal analysis, and next-generation intelligent biosensors.
“This research presents a foundational technology that integrates biosignal detection and neuromorphic computation into a single device,” said Professor Yoo Ho-cheon. “It holds great promise for low-power, high-density healthcare monitoring systems, next-generation biosensors, and wearable healthcare platforms.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) under the ICT Human Resource Development Program for AI Semiconductors. The research findings were published in the August 2025 issue of Small, a leading international journal in materials science and electronic devices. Upon publication, the paper was selected as the journal’s “Editor’s Choice” for its excellence.
The article, titled “DPP-DTT Nanowire Phototransistors for Optoelectronic Synapses in EMG and ECG Signal Classification,” lists Choi Wang-myung (Ph.D. candidate) and Lee Won-woo (integrated master’s and Ph.D. student) as co-first authors, with Professor Yoo serving as the corresponding author.

 '한양위키' 키워드 보기
'한양위키' 키워드 보기